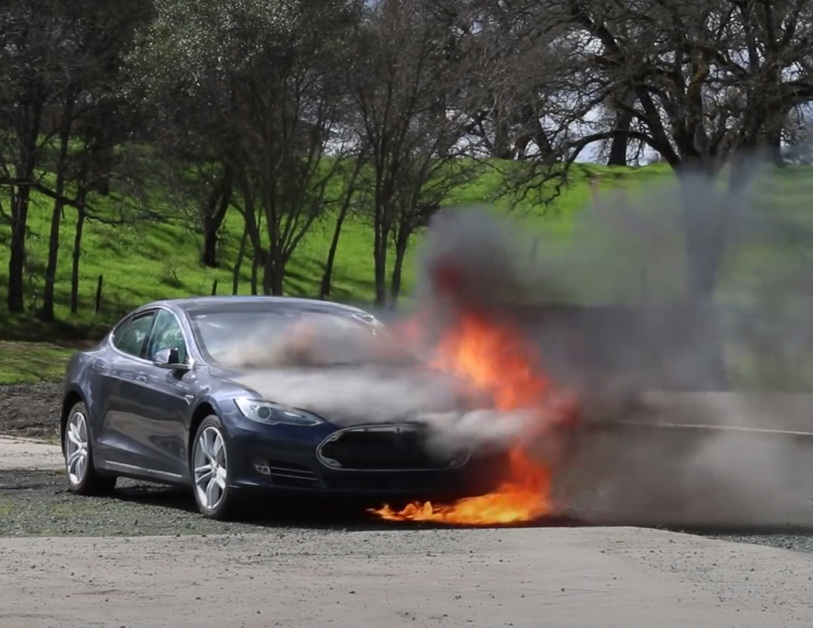

The answer is no. Based on research by AutoinsuranceEZ, it is five times more likely that a fossil-fueled vehicle will catch fire than an electric vehicle. Hybrid cars with both a high voltage battery and an internal combustion engine have a 3.4% likelihood of vehicle fires according to the same study.
However, when fires do happen, electric vehicles with lithium-ion batteries burn hotter and faster. And the batteries can re-ignite hours or even days after the fire is initially controlled.
Thermal runaway, or thermal propagation, begins when the heat generated within a lithium-ion battery exceeds the amount of heat that is dissipated to its surroundings. This can happen due to overcharging, physical damage to the battery cell, short circuits, or because of high temperatures.
Lithium batteries are extremely sensitive to high temperatures and inherently flammable. They are known to reignite hours, days, or even weeks after the initial burst – and can do so several times.
Which factors can start a fire in a lithium-ion battery?

It is an unfortunate myth that thermal propagation can be controlled with water. The only way to extinguish a fire in a lithium battery is to cool down the battery.
One example is using water to cool down the batteries while lifting the burning vehicle to reach the area where the batteries are located. This method requires a lot of water and is time-consuming.
This method usually has a limited effect due to the construction of EVs with several insulating layers of metal and air.
Another major problem with using water is the contamination of air and groundwater when thousands of liters of water seep into the ground.
Pouring water on the fire or an already overheated battery can actually make the situation worse, and cause short circuits in several places in the batteries.
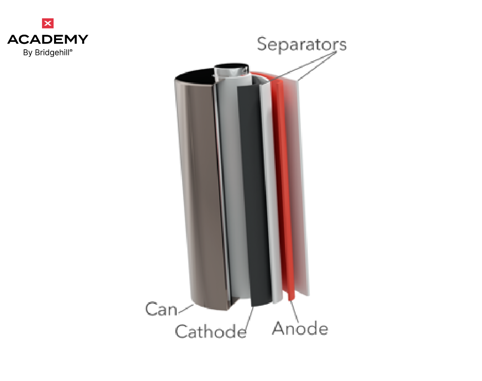
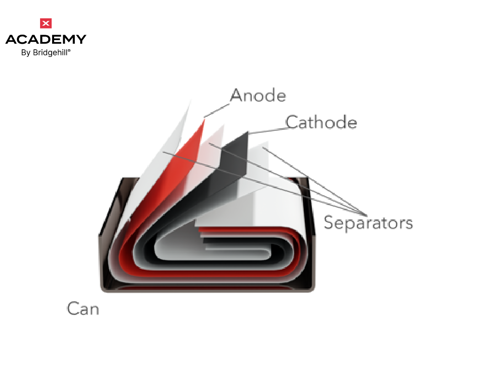
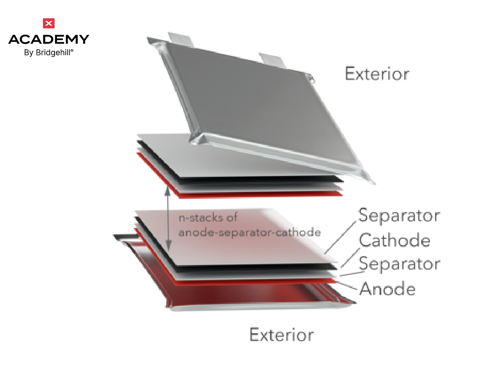
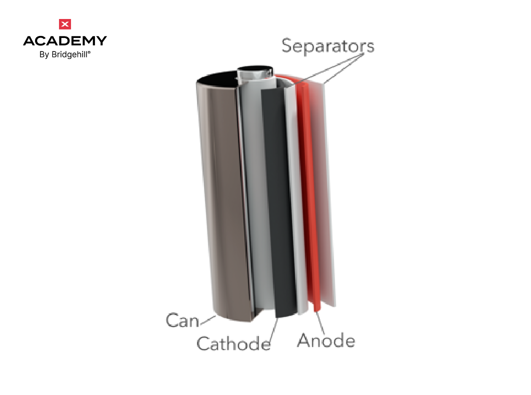
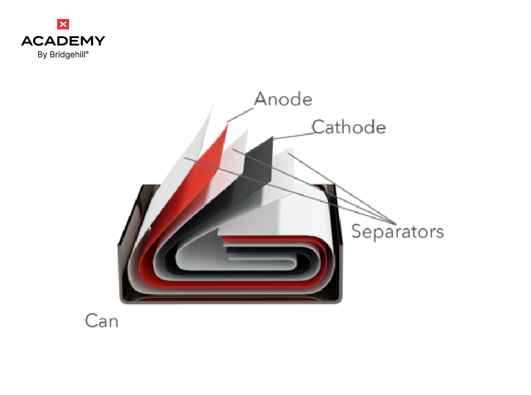
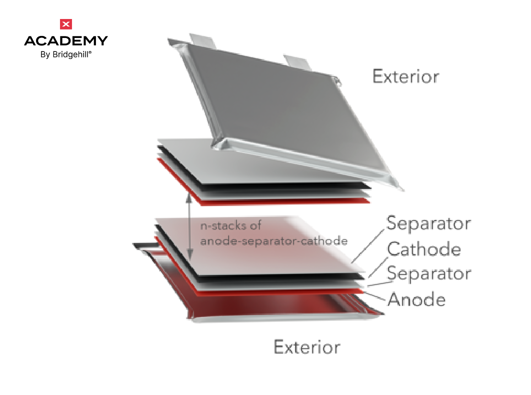
Solid-state batteries could be a game changer for electric vehicles because they can charge faster and store more energy than lithium-ion batteries. It actually stores 2-2.5 times more energy at the same volume as lithium-ion batteries do.
In addition, solid-state batteries are also lighter, tend to be less flammable and can withstand more physical damage than lithium-ion batteries. Which means more powerful and longer range electric vehicles, or more compact and lighter.
However, solid-state batteries cannot withstand water when damaged, as the lithium metal is an element that naturally catches fire in contact with water! Watch the film below to see how it reacts to water.


